Code fusion is a web development learning blog youtube channel
Showing posts with label dbms. Show all posts
Showing posts with label dbms. Show all posts
Wednesday, 15 October 2014
Lesson 19 Aggregation
Aggregation is the process of compiling
information on an object, there by abstracting a higher level object. One
limitation of E-R model is that it cannot express relationship with in
relationship to illustrate the need for such a construct the ternary (compose of three) relationship work_on,
between employee branch job so in figure. Thus the relationship set work_on
relating the entity set, such an entity set is treated in the same manner as in
any other entity set. We can then created a binary relationship manager to
represent who manage what task
Tuesday, 14 October 2014
Lesson 18 What is class and object
What is class?
Class is a set of object that share common structure
and common behaviour is called class.
For example
Flora, fauna, flower, animal, bird etc..
What is object?
An object is something that has a fixed set of well
define boundary. If you look at your computer disk you would object varying
descriptions
For example
&Note
In ordinary sense, an object is something which can be seen, touch or sensed.
Monday, 13 October 2014
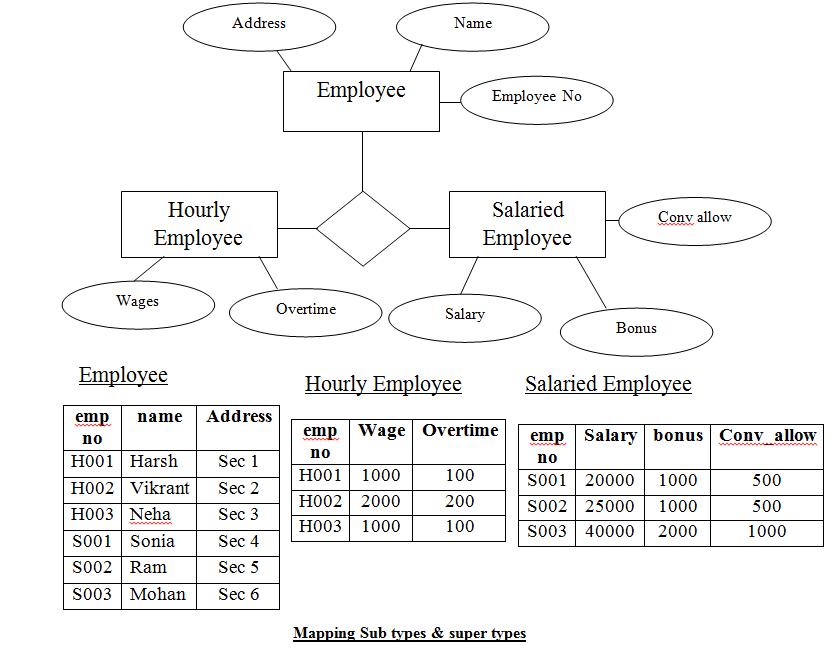
Lesson 16 Generalization
Now consider the opposite of above example. Two
entities saving account and current account have some attribute
that are common. In this case, a better option
is to create a new separately to simplify multiple references. This is called generalization.
&Note
Generalization
is the result of taking the union of two or more lower level entity set to
produce higher level entity set.
Sunday, 12 October 2014
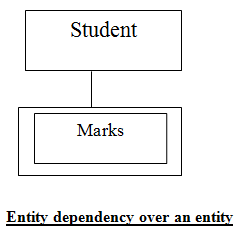
Lesson 12 Strong & weak entity
Database design using E-R Model
A database which conforms to an ER diagram can
be represented by a set of tables.
Strong & weak entity
These are two type of entity mainly dependent entity
(also called weak entity) and
independent entity also (called regular
entity and weak entity).
The
dependent entity is the one whose existence dependents on another entity. An entity set is called weak entity set if its
existence depends on the existence of another weak entity or any other strong
entity. A weak entity set does not have sufficient attributes to form a
primary key.
Note => A weak entity
set represented by double outline rectangle in ER diagram.
Consider
an entity type marks which represent the marks obtained by student. Now the
existence of marks dependence upon the existence of entity type student.
&Note
A weak entity set can be converted to strong
entity set by adding appropriate attributes.
Let’s take real life situation to understand
type of entity. Suppose a student says ‘Swati’
can have many instance of marks say eng_marks;
sci_marks; sst_marks etc. related to it if instance ‘Swati’. If Swati is deleted then all the entity marks dependent
upon swati will also removed.
Marks
is dependent (weak) entity that is dependent on entity student.
For example
The entity
Employee & Student are strong entity they have the primary keys Emp_no
& admin no
&Note
An
entity set which has primary key termed as a strong entity set
your review is very important to us for better quality.
Please Comment
Tuesday, 24 September 2013
Lesson 11 Why we use Entity Relationship diagram ERD
"They are actually true. What is the use of this Subject. If you say its too late to explain this I would be post this dialog early posting some where."
"You may be right but in my point of view you know nothing about this Topic. Now we are moving to advance level actually its is the best time to chat with you guys. So let me explain.."
what is dbms actually all about.
I have good example...
My dear friends you are reading my blog. So you Know about computer programming as well Let us assume that.. well i am sure about it!
Then you surely heard about algorithms in programming.
Algorithms are some thing like frame setup for an complex programming.
simply in Alogo (aka) we decide how to develop a program, whats the structure of the program. how many veritable are used in a program. what approach we should take to solve the problem.
ERD is an algorithms in software development or designing. Let me explain more clearly by an other example.
Assume You are the Owner of a software development company Let's Name it Sam enterprises
Now I come to you having a small school. I want to upgrade my
school. hand work to computerization.
If you know only programming You are not able to handle it.
So Entity relationship model is just a Blueprint of a client
organization..
you better understood later lessons.
Tuesday, 17 September 2013
Sunday, 24 February 2013
Lesson 8 Many to Many M:M
Lesson 8
c) Many to Many (M:M)
A many to many relationship describe entities that may have many relationship among each other
For example
I. One customer may buy many items and one item may be bought by many customers.
II. A student can take many courses in university and many students can register for given course.
 |
Thursday, 21 February 2013
Lesson 7 One to many 1:m
b) One
to many (1:m)
One to many relationships exists when one
entity is related to more than one entity. For example:-
1.
Father may have many children
but a child have only one father.
2.
Two
entities set namely courses & teacher, if you assume that more than
one Subject or course is taught by a
teacher, and then a relationship is
one to many between teacher & courses.
Sunday, 17 February 2013
Lesseon 6 One to One
These are:
a) One to one (1:1)
b) One to many (1:m)
c) Many to many (m:m)
a) One to one (1:1)
A one to one (1:1) relationship is an association only between two entities.
For example, in a university each department has only one head of department. More over one faculty member cannot be the head of more than one department.
This shows one to one relationship between departments as head.
Another example of such relationships is between automobile & engine. If we assume that a car does not have two engines and that car must be filter with one engine in car.
your review is very importent to us for better quality.
Please Comment me Below or E-mail me @ harshkumar2009@gmail.com
Friday, 15 February 2013
Lesson 5 Relationship
To understand what we mean by relationship among data item, we need some familiarity with data model terminology. An entity is a thing which can be easily identified.
It may be an object, place, person, concept or activity for which data need to be recorded.entity of student instructor
Note
An association among entity lead to relationship.
Example
There is some relationship between instructor and student as seen in figure
Your review is very important to us for better quality.
Please Comment me Below
Lesson 1 INTRODUCTION TO DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Introduction
Database is an organized collection of fact. In other word we can say that it is collection of information arranged and presented to serve and assigned purpose.
An example of Database is a dictionary, where word arranged alphabetically. Another example is telephone directory.
Note
Thus information is stored and arrange in a particular manner
Note
Thus information is stored and arrange in a particular manner
In order to keep database update we may need to perform operations like:-
- Adding information
- Removing information
- Editing the existing information
Why database in used?
Any organization be it a bank, manufacturing company, hospital, university, government department; required huge amount of data in same form or the other all such organization need to collect data, manipulate them and store them for future use.
Characteristics of Database
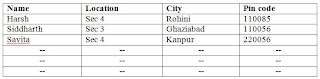
Fields: The smallest piece of meaningful information of file is called a database item or field. A database item is generally use for a group alpha numeric character.
A data item is generally used for a group of alpha numeric character figure display the data item, fields in records.
NAME, LOCATION, CITY, PIN CODE
Records: The collection of related field is called records.
Files: A collection of record is called files
Thursday, 14 February 2013
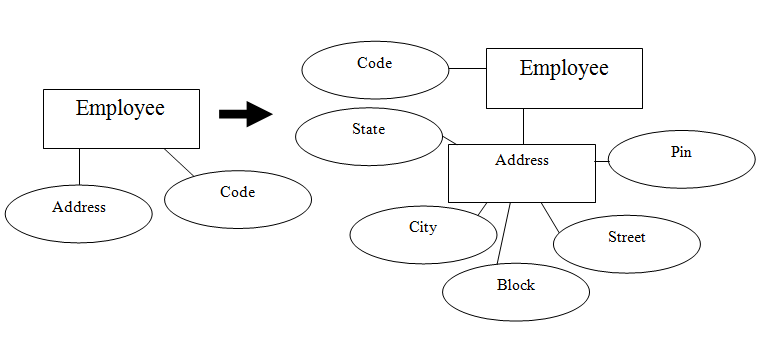
Lesson 4 Attribute
2.Attribute
Each property or attribute show in the ER diagram map to an attributes in the appropriate time (refer to the following figure). Properties or attributes of STUDENT & BOOKS map to attributes in the relevant table
>Note
Remember that the primary key must be able to uniquely identify each tuple in table.
Wednesday, 13 February 2013
Lesson 3 Mapping E-R diagram to table
A database that conforms to an ER diagram can be represented by a collection of table in the relational system.
1. Regular Entity
2. Attributes
3. Relationship
4. Weak Entity
5. Subtype & super type
1. Regular Entity You will recall entity are dependent, they can exist in isolation, independent of any other blocks of database. Each regular entity maps to table.
WE ALWAYS GET PUZZLED IN DIFFERENT WORDS BUT WITH THE SAME MEANING.
Please Comment me Below or E-mail me @ harshkumar2009@gmail.com
Lesson 2 Entity Relationship Model
The Entity Relationship Model consist of the following component
• Person: - Employee, Student, Vender….
• Place: - Branch, Office, Building, room….
• Object: - Book, Machine, Pen…..
• Event: - Sell, Purchase, Registration…
roll number is a property of an entity student.
NOTE
In dbms there are many words for a same thing
means as above i said field and then I said entity, some time its called columns, DON'T GET PUZZLED IN THAT
this is only the way some kind of differentiating different environments
for example ROWS, RECORDS and TUPLES
If you talking in RDBMS (Relational Data Base Management System) we called them TUPLES.
If you talking in DBMS (Data Base Management System) we called them RECORDS.
If you talking in MS EXCELL we called them ROWS.
=========================================
Column, Fields, Attributes
Column :- In EXCELL
Fields:- In DBMS
Attributes:- in E-R DIGRAM
=======================================
Entity, Table, File
Entity:- In E-R DIGRAM
Table :- When we create/edit an ENTITY in form of Table.
File :- when data stored in hardware (hard disk)
WE ALWAYS GET PUZZLED IN DIFFERENT WORDS BUT WITH THE SAME MEANING.
Please Comment me Below or E-mail me @ harshkumar2009@gmail.com.
a) Entity
b) Attributes
c) Relationship
d) Key Attributes
b) Attributes
c) Relationship
d) Key Attributes
a) Entity
An entity is class object event or concepts about which we need collect and store data.
An entity is class object event or concepts about which we need collect and store data.
- note
• Person: - Employee, Student, Vender….
• Place: - Branch, Office, Building, room….
• Object: - Book, Machine, Pen…..
• Event: - Sell, Purchase, Registration…
b) Attributes An attributes is a property of given entity.
NOTE
In dbms there are many words for a same thing
means as above i said field and then I said entity, some time its called columns, DON'T GET PUZZLED IN THAT
this is only the way some kind of differentiating different environments
for example ROWS, RECORDS and TUPLES
If you talking in RDBMS (Relational Data Base Management System) we called them TUPLES.
If you talking in DBMS (Data Base Management System) we called them RECORDS.
If you talking in MS EXCELL we called them ROWS.
=========================================
Column, Fields, Attributes
Column :- In EXCELL
Fields:- In DBMS
Attributes:- in E-R DIGRAM
=======================================
Entity, Table, File
Entity:- In E-R DIGRAM
Table :- When we create/edit an ENTITY in form of Table.
File :- when data stored in hardware (hard disk)
WE ALWAYS GET PUZZLED IN DIFFERENT WORDS BUT WITH THE SAME MEANING.
Please Comment me Below or E-mail me @ harshkumar2009@gmail.com.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)